
What is a right-lateral fault?
Left-lateral fault strike slip fault with low friction along fault contact. There is no deformation of the rock adjacent to contact. If the block opposite an observer looking across the fault moves to the left, the motion is termed left lateral. Example: the San Andreas Fault of California

Animation shows the buildup of stress along the margin of two stuck plates that are trying to slide past one another. Stress and strain increase along the contact until the friction is overcome and rock breaks.

Left-lateral fault strike slip fault with little or no friction along fault contact. There is no deformation of the rock adjacent to contact. If the block opposite an observer looking across the fault moves to the left, the motion is termed left lateral.

In a strike-slip fault, the movement of blocks along a fault is horizontal. The fault motion of a strike-slip fault is caused by shearing forces. Other names: transcurrent fault, lateral fault, tear fault or wrench fault. Examples: San Andreas Fault, California; Anatolian Fault, Turkey.
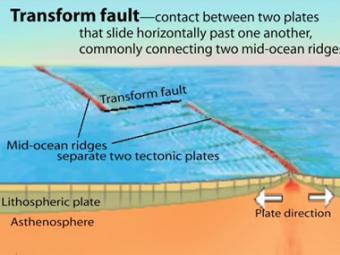
A transform fault is a type of strike-slip fault wherein the relative horizontal slip is accommodating the movement between two ocean ridges or other tectonic boundaries. They are connected on both ends to other faults.