6min 40s Novice Spanish

What does the historic record tell us about earthquakes in the area?
Hispaniola straddles four plates: the Caribbean Plate and the Gonâve, Hispaniola, and North Hispaniola microplates. It is caught in the crunch between the North American and Caribbean Plates. Hispaniola has had a long history of deadly earthquakes, including the most recent one near Port au Prince in 2010. North of Hispaniola the North American plate has a more difficult time subducting because the Bahamas Carbonate Platform with limestone reef deposits up to 6-km-thick have doubled the crustal thickness with more-buoyant material that resists subduction.
CLOSED CAPTIONING: A .srt file is included with the download. Use an appropriate media player to utilize captioning.

On the tenth anniversary of the January 12, 2010 magnitude 7.0 earthquake in Haiti, it is important to reflect on the plate tectonic context and human impact of that event.
This earthquake was five times more fatal than any historical magnitude 7 earthquake and the fourth most lethal earthquake of any magnitude in the last 100 years.
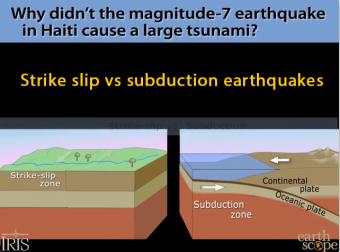
Strike-slips faults like the one that devastated Haiti don't generally cause tsunami, except for small local ripples. The Haiti earthquake was a horizontal motion. Tsunamis are caused by either an uplifting of the ocean floor, or by a huge chunk of land sliding into the ocean. Subduction-zone earthquakes raise the ocean bottom suddenly to push the water in tsunamis.

Jamaica straddles the Caribbean Plate and the Gonâve Microplate, the largest of four microplates that are caught in a crunch between the North American and Caribbean Plates. Jamaica has had a long history of deadly earthquakes.

Lithospheric plates are part of a planetary scale thermal convection system. The energy source for plate tectonics is Earth’s internal heat while the forces moving the plates are the “ridge push” and “slab pull” gravity forces.
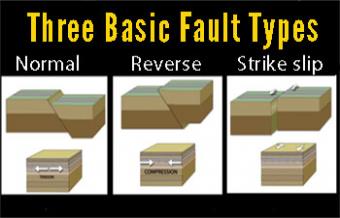
[updated 2021] A fault is a rock fracture where the two sides have been displaced relative to each other. Faults are categorized into three general groups based on the sense of slip or movement: normal, reverse, and strike-slip.
This clip includes selected excerpts from the animation, "Earthquake Faults, Plate Boundaries, & Stress".