Seismic Waves is a browser-based tool to visualize the propagation of seismic waves from historic earthquakes through Earth’s interior and around its surface. Easy-to-use controls speed-up, slow-down, or reverse the wave propagation. By carefully examining these seismic wave fronts and their propagation, the Seismic Waves tool illustrates how earthquakes can provide evidence that allows us to infer Earth’s interior structure. Narrated by John Taber, Director of Education and Public Outreach, IRIS The Seismic Waves tool was produced through a collaboration between Alan Jones & Jeff Baker (Binghamton University) and IRIS EPO.
Seismic Waves is a browser-based tool to visualize the propagation of seismic waves from historic earthquakes through Earth’s interior and around its surface. Easy-to-use controls speed-up, slow-down, or reverse the wave propagation. By carefully examining these seismic wave fronts and their propagation, the Seismic Waves tool illustrates how earthquakes can provide evidence that allows us to infer Earth’s interior structure.
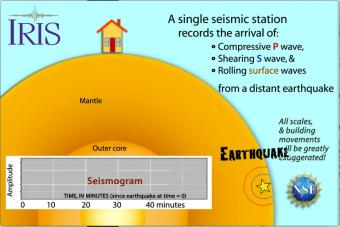
Seismic waves travel through the earth to a single seismic station. Scale and movement of the seismic station are greatly exaggerated to depict the relative motion recorded by the seismogram as P, S, and surface waves arrive.
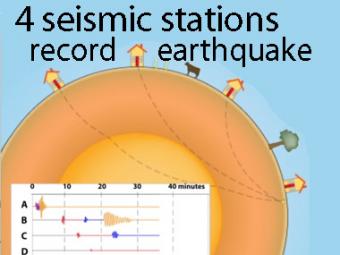
A cow and a tree in this narrated cartoon for fun and to emphasize that seismic waves traveling away from an earthquake occur everywhere, not just at seismic stations A, B, C, and D. A person would feel a large earthquake only at station A near the epicenter. Stations B, C, D, and the cow are too far from the earthquake to feel the seismic waves though sensitive equipment records their arrival.
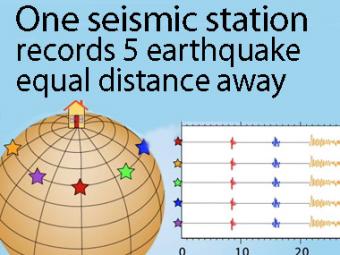
A gridded sphere is used to show a single station recording five equidistant earthquakes.
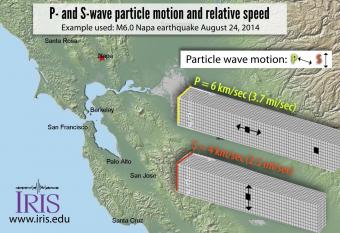
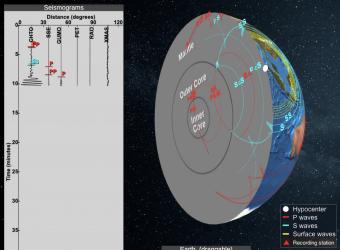
When an earthquake occurs, seismic waves, including P and S waves carry energy away from the hypocenter in all directions. This video explores how the difference in the P and S waves results in staggered arrivals that, in turn, provides information about how far away the earthquake was from the seismograph.
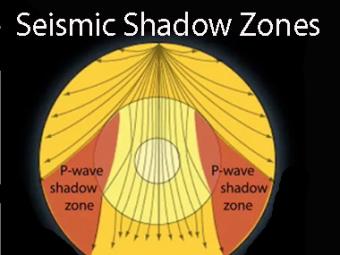
Seismic shadow zones have taught us much about the inside of the earth. This shows how P waves travel through solids and liquids, but S waves are stopped by the liquid outer core.