1min 48s Novice Spanish
How do P & S waves give evidence for a liquid outer core?
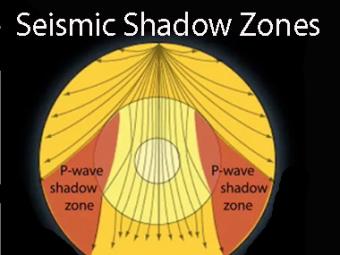
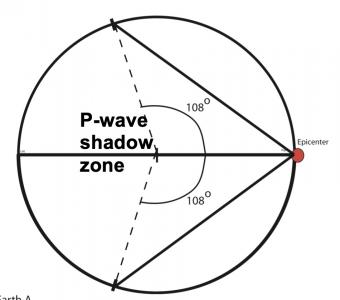
The seismic shadows are the effect of seismic waves striking the core-mantle boundary. P and S waves radiate spherically away from an earthquake's hypocenter (or focus) in all directions and return to the surface by many paths. S waves, however, don't reappear beyond an angular distance of ~103° (as they are stopped by the liquid) and P waves don't arrive between ~103° and 140° due to refraction at the mantle-core boundary.
CLOSED CAPTIONING: A .srt file is included with the download. Use an appropriate media player to utilize captioning.

Seismic shadow zones have taught us much about the inside of the earth. This shows how P waves travel through solids and liquids, but S waves are stopped by the liquid outer core.

The wave properties of light are used as an analogy to help us understand seismic-wave behavior.
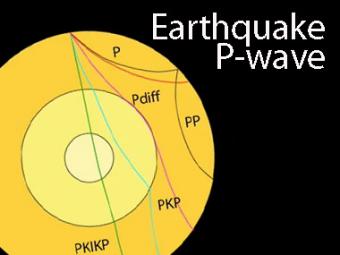
The shadow zone is the area of the earth from angular distances of 104 to 140 degrees from a given earthquake that does not receive any direct P waves. The different phases show how the initial P wave changes when encountering boundaries in the Earth.
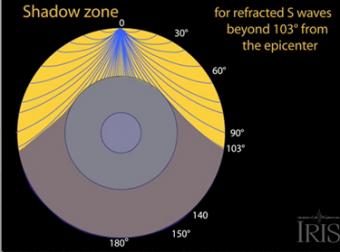
The shadow zone results from S waves being stopped entirely by the liquid core. Three different S-wave phases show how the initial S wave is stopped (damped), or how it changes when encountering boundaries in the Earth.
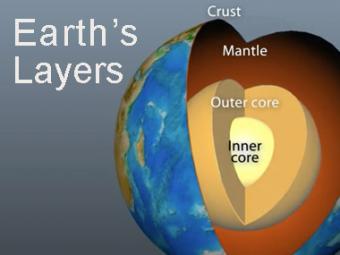
The Earth has 3 main layers based on chemical composition: crust, mantle, and core. Other layers are defined by physical characteristics due to pressure and temperature changes. This animation tells how the layers were discovered, what the layers are, and a bit about how the crust differs from the tectonic (lithospheric) plates, a distinction confused by many.
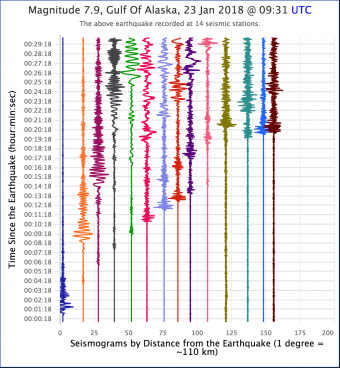
Learning occurs as students work first in small groups and then as a whole class to compare predicted seismic wave travel times, generated by students from a scaled Earth model, to observed seismic data from a recent earthquakes. This activity uses models, real data and emphasizes the process of science.
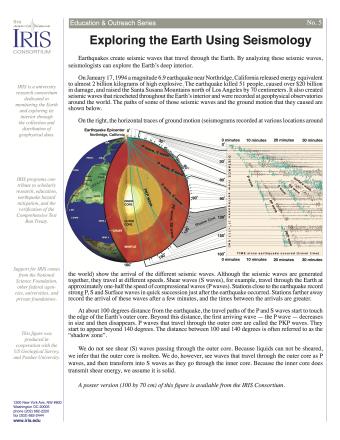
Earthquakes create seismic waves that travel through the Earth. By analyzing these seismic waves, seismologists can explore the Earth's deep interior. This fact sheet uses data from the 1994 magnitude 6.9 earthquake near Northridge, California to illustrate both this process and Earth's interior structure.
NOTE: Out of Stock; self-printing only.
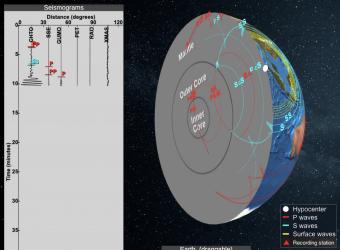
Seismic Waves is a browser-based tool to visualize the propagation of seismic waves from historic earthquakes through Earth’s interior and around its surface. Easy-to-use controls speed-up, slow-down, or reverse the wave propagation. By carefully examining these seismic wave fronts and their propagation, the Seismic Waves tool illustrates how earthquakes can provide evidence that allows us to infer Earth’s interior structure.
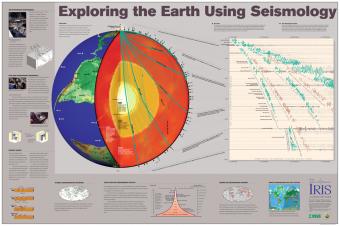
Seismic waves from earthquakes ricochet throughout Earth's interior and are recorded at geophysical observatories around the world. The paths of some of those seismic waves and the ground motion that they caused are used by seismologists to illuminate Earth's deep interior.