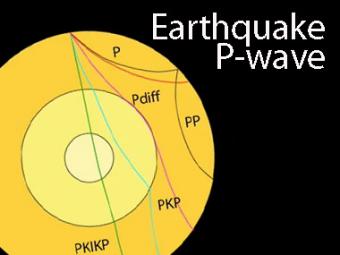
How do P waves give information about Earth's core?
Animation addresses 5 common variations of P-type seismic body waves. All are compressive waves that travel through the Earth in all directions away from the epicenter of an earthquake. The different phases show how the initial P wave changes when encountering boundaries in the Earth.
CLOSED CAPTIONING: A .srt file is included with the downloiad. Use appropriate media player to utilize captioning.
Information about Earth's deep interior is derived from seismic waves:
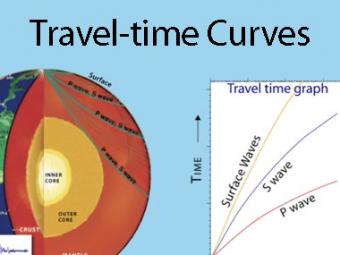
A travel time curve is a graph of the time that it takes for seismic waves to travel from the epicenter of an earthquake to the hundreds of seismograph stations around the world. The arrival times of P, S, and surface waves are shown to be predictable. This animates an IRIS poster linked with the animation.
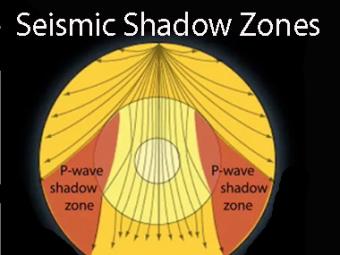
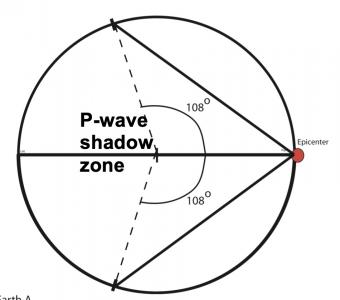
Seismic shadow zones have taught us much about the inside of the earth. This shows how P waves travel through solids and liquids, but S waves are stopped by the liquid outer core.

The wave properties of light are used as an analogy to help us understand seismic-wave behavior.

Seismic tomography is an imaging technique that uses seismic waves generated by earthquakes and explosions to create computer-generated, three-dimensional images of Earth's interior. CAT scans are often used as an analogy. Here we simplify things and make an Earth of uniform density with a slow zone that we image as a magma chamber.
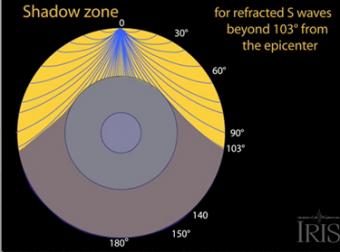
The shadow zone results from S waves being stopped entirely by the liquid core. Three different S-wave phases show how the initial S wave is stopped (damped), or how it changes when encountering boundaries in the Earth.
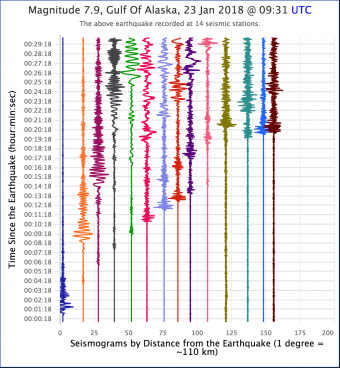
Learning occurs as students work first in small groups and then as a whole class to compare predicted seismic wave travel times, generated by students from a scaled Earth model, to observed seismic data from a recent earthquakes. This activity uses models, real data and emphasizes the process of science.
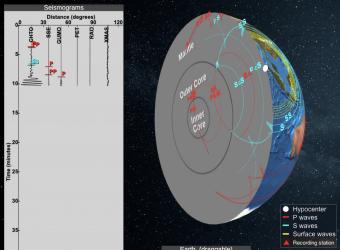
Seismic Waves is a browser-based tool to visualize the propagation of seismic waves from historic earthquakes through Earth’s interior and around its surface. Easy-to-use controls speed-up, slow-down, or reverse the wave propagation. By carefully examining these seismic wave fronts and their propagation, the Seismic Waves tool illustrates how earthquakes can provide evidence that allows us to infer Earth’s interior structure.