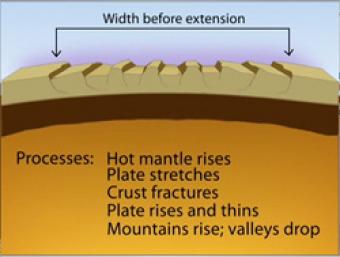
How do basin and range mountains and valleys form?
The basins (valleys) and ranges (mountains) are being created by ongoing tension in the region, pulling in an east-west direction. Over most of the last 30 million years, movement of hot mantle beneath the region caused the surface to dome up and then partially collapse under its own weight, as it pulled apart. If it continues to pull apart, it could create a spreading ridge with an intervening ocean. Currently, there is very little actual stretching going on, and the small amount is concentrated on the western and eastern edges of the Basin-Range.
CLOSED CAPTIONING: A .srt file is included with the download. Use an appropriate media player to utilize captioning.
Basin & Range province
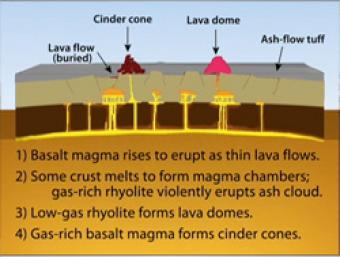
During Basin & Range extension, the plates pull apart, the mantle rises and melts due to lower pressures near the surface. The style of eruption depends on how long the magma sits in the crust and undergoes processes such as crystallization and melting and assimilation of wall rock.
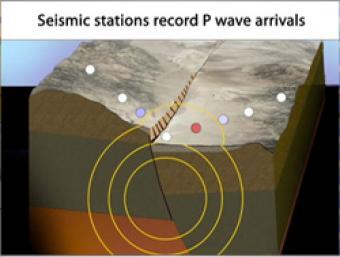
Cross section of the shallow crust in the Basin & Range. Earthquake produces seismic waves that bump an array of seismic stations. One station records the arrival of the seismic waves on a seismogram.
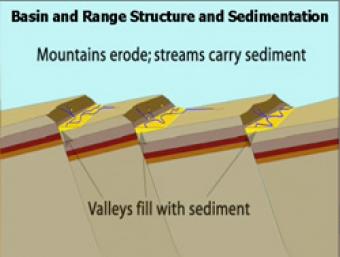
As extension and uplift occur, erosion and sedimentation happen simultaneously but at slower rates. As extension slows down, erosion and sedimentation can overcome mountain building.

Stratigraphy is the branch of geology that studies rock layers; structure includes the faults and folds that result from regional & local forces acting on the area. A hypothetical cross section is studied by going back to the beginning to study its progressive geologic history.

How can I demonstrate plate tectonic principles in the classroom?
Video lecture demonstrates the use of foam faults to demonstrate faults, and a deck of cards to demonstrate folds and fabrics in rock layers. Different types of faults include: normal (extensional) faults; reverse or thrust (compressional) faults; and strike-slip (shearing) faults.
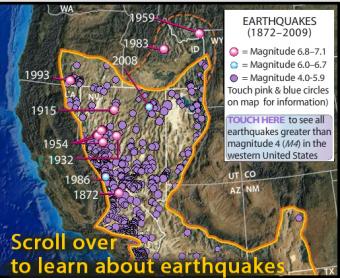
Interactive map reveals seismology, geology, and geologic history of the midwest.
(IRIS is going to discontinue Flash animations in 2020)
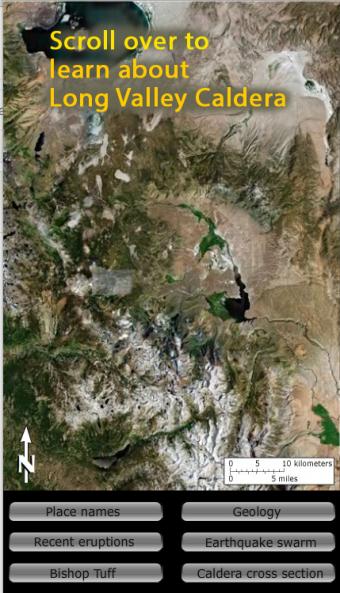
Long Valley Caldera area has had a history of eruptions and earthquake swarms. Learn more with this interactive map that reveals geology, eruptions, earthquakes, and more.

This interactive map of the Basin and Range Province reveals earthquakes, faults, hazards, volcanoes, mines, and National Parks.
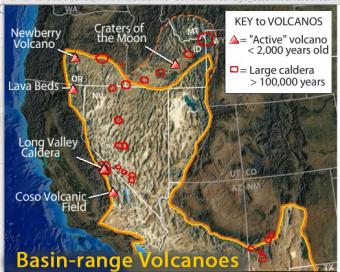
This interactive map of the Basin-Range Province reveals information about the youngest volcanic features associated with the region.